-
Thermodynamics, Structure and Properties of Polynuclear Lanthanide Complexes with a Tripodal Ligand: Insight into their Self-Assembly
J. Hamacek, C. Besnard, T. Penhouet and
Chemistry - A European Journal, 17 (24) (2011), p6753-6764


DOI:10.1002/chem.201100173 | unige:17236 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
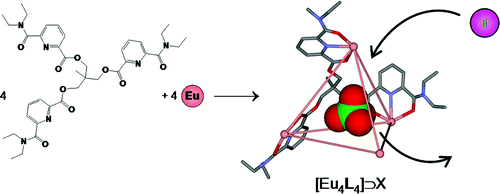
Self-assembly processes between a tripodal ligand and LnIIIÂ cations have been investigated by means of supramolecular analytical methods. At an equimolar ratio of components, tetranuclear tetrahedral complexes are readily formed in acetonitrile. The structural analysis of the crystallographic data shows a helical wrapping of binding strands around metallic cations. The properties of this series of highly charged 3D compounds were examined by using NMR spectroscopy and optical methods in solution and in the solid state. In the presence of excess metal, a new trinuclear complex was identified. The X-ray crystal structure elucidated the coordination of metallic cations with two ligands of different conformations. By varying the metal/ligand ratio, a global speciation of this supramolecular system has been evidenced with different spectroscopic methods. In addition, these rather complicated equilibria were successfully characterised with the thermodynamic stability constants. A rational analysis of the self-assembly processes was attempted by using the thermodynamic free energy model and the impact of the ligand structure on the effective concentration is discussed.